MONDY Nathalie PU
Enseignant chercheur : E2C
Directrice du LEHNA : Pôle de Direction
Université Lyon 1
CNRS, UMR 5023 - LEHNA,
Laboratoire d'Ecologie des Hydrosystèmes Naturels et Anthropisés
3, rue Raphaël Dubois - Bât. Darwin C
F-69622 Villeurbanne Cedex FRANCE
(+33) 04 72 43 29 53
Cette adresse e-mail est protégée contre les robots spammeurs. Vous devez activer le JavaScript pour la visualiser.


Mon domaine de recherches
Mes travaux de recherche se situent dans le cadre de l’écophysiologie évolutive afin de comprendre les règles physiologiques et/ou comportementales qui permettent aux organismes d’optimiser leurs traits d’histoire de vie en fonction des contraintes environnementales. Comprendre le rôle de ces contraintes sur la dynamique des populations implique l'étude des facteurs physiologiques intervenant dans la modulation des compromis évolutifs (survie /reproduction, reproduction immédiate / reproduction future, immunité / signaux sexuels…).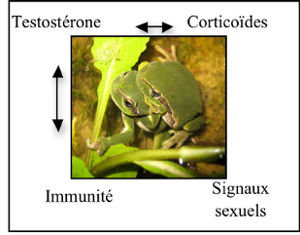 Thème 1 - Mécanismes endocrines et sélection sexuelle chez la rainette arboricole, Hylaarborea
Thème 1 - Mécanismes endocrines et sélection sexuelle chez la rainette arboricole, Hylaarborea
Collaborateurs : J. Desprat, T. Lengagne, L. Teulier, C. Romestaing, A. Dumet, E. Desouhant, M. Troianowsky
Dans le cadre de la sélection sexuelle, les femelles choisissent leurs mâles en estimant leurs qualités via les signaux sexuels qu’ils émettent. Ces signaux sont qualifiés d’honnêtes dans la mesure où ils reflètent la condition corporelle et l’état sanitaire des mâles. Ce projet a pour but d’établir le rôle de la testostérone sur 1) la production de signaux acoustiques et visuels et 2) le statut immunitaire chez les mâles de rainette arboricole. Dans un deuxième temps, l’impact d’une pollution sonore générant une augmentation de glucocorticoïdes sur l’ensemble du système a été étudiée.
Pour en savoir plus :
Desprat, et al., 2015. Behavioural Ecology 26: 1138-1146
Troïanowski et al., 2015. Behaviour, 152, 821-836.
Josserand et al., 2015. Amphibia-Reptila, 36, 111-118.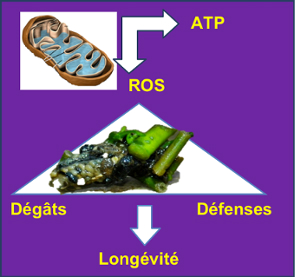
Thème 2 – Coûts et bénéfices de la construction de fourreaux par les Trichoptères
Collaborateurs : S. Puijalon, Y. Voituron, B. Rey, A. Dumet
Le programme de recherches, que je mène a permis de montrer que l’activité de construction d’un fourreau chez un trichoptère (Limnephilus rhombicus) provoque une augmentation du métabolisme aérobie de la larve et du stress oxydant et induit un coût immédiat et différé chez l’adulte. Actuellement, je cherche i) à déterminer quels sont les mécanismes physiologiques qui contrôlent ce coût post-métamorphose (régulation hormonale…) et ii) à préciser comment les animaux optimisent le ratio coût/résistance en utilisant des matériaux variés.
Pour en savoir plus :
Mondy et al., 2011. Journal of Insect Physiology, 57, 197-202.
Mondy et al., 2012. Journal of Experimental Biology, 215, 3453-3458.
Thème 3 – Impact de l’urbanisation sur les populations animales (comportement et physiologie)
Récemment, j’ai initié plusieurs études afin de comprendre comment l’apparition de nouvelles contraintes environnementales pour les animaux qui vivent en milieu urbain ou périurbain affecte leur physiologie et au-delà leur fitness.
1 – Etude de l’impact de l’urbanisation (îlots de chaleur urbain et métaux lourds) sur les communautés de fourmis
Collaborateurs : J. Gippet, B. Kaufmann
2 – Etude de l’impact de la pollution lumineuse sur la physiologie d’un anoure
Collaborateurs : J. Secondi, T. Lengagne, M. Théry
Mes activités passées
1 - Dynamique ovarienne chez un parasitoïde synovigénique Afin d’étudier le compromis entre reproduction immédiate ou reproduction future, à l’aide de manipulations expérimentales d’un système tri-trophique (plante, insecte, parasitoïdes), nous avons montré l’importance des stérols et de l’ecdysone dans le maintien de la plasticité de l’ovogenèse permettant aux parasitoïdes de maximizer leur reproduction dans un environnement imprévisible.
Afin d’étudier le compromis entre reproduction immédiate ou reproduction future, à l’aide de manipulations expérimentales d’un système tri-trophique (plante, insecte, parasitoïdes), nous avons montré l’importance des stérols et de l’ecdysone dans le maintien de la plasticité de l’ovogenèse permettant aux parasitoïdes de maximizer leur reproduction dans un environnement imprévisible.
Pour en savoir plus :
Mondy et al., 2006. Journal of Insect Physiology, 52, 897-904
Bodin et al., 2007. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 65, 103-111.
Bodin et al., 2009. Journal of Insect Physiology, 55, 643-648.
Plus d’informations : équipe relations multitrophiques, Pr J. CasasNous avons étudié la réponse physiologique des poireaux induite par l’attaque des larves d’un microlépidoptère afin de déterminer si cette réponse est un système de défense induit indirect. L’originalité de ce modèle réside dans la nature soufrée des composés secondaires volatils produits par la plante en réponse à des stress biotiques. 2 – Etude des mécanismes de défense induite chez les Allium
2 – Etude des mécanismes de défense induite chez les Allium
Pour en savoir plus :
Mondy et al., 2001. Chromatographia, 53, 356-360
Mondy et al., 2002. J. Chromatogr. A, 963, 89-93
Dugravot et al., 2005.J. Chemical Ecol., 31, 1287-1302Ce travail à fait l’objet de la thèse de S. Dugravot
3 - Bases biochimiques de la relation mutualiste entre un champignon phytopathogène et un insecte ravageur du vignoble (INRA, UMR 1065)
Au cours de mon doctorat, j’ai travaillé sur l’interaction mutualiste entre un champignon pathogène (Botrytis cinerea) et un insecte phytophage (Lobesia botrana) dans l’agro-écosystème viticole. Des expérimentations menées en conditions naturelles et au laboratoire, ont démontré que l’ingestion de mycélium par les larves induit une augmentation de la fitness globale de l’insecte (diminution de la durée du développement larvaire, augmentation de la survie larvaire et de la fécondité des femelles) du fait de la présence de stérols fongiques particuliers.
Pour en savoir plus :
Mondy et al., 1998. Entomologia Exp. App., 88: 1-7
Mondy et al., 1998. Compte Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences (série III), 321 : 665-671
Mondy N., Corio-Costet M-F. 2000. J. Insect, Physiol., 46, 1557
PDF des articles sur demande.- Responsabilités :
Responsable de la plateforme enseignement « Ecologie et Biologie des Organismes »
plus d’infos : http://umr5023.univ-lyon1.fr/equipes-techniques/pole-pedagogique-ebo
Responsable de l’UE Biologie des Organismes en L1 (UE BO1)
Enseignements :
Biologie animale (Biologie des organismes, Biologie et Ecologie des Organismes, Grandes fonctions animales, Zoologie)
Ecophysiologie (Ecophysiologie et vie en milieux extrême)
Entomologie agricole et urbaine (Licence Pro ATIB)
Ecologie (Ecologie des communautés) - Sous Presse Dasque, L., Roussel, D., Bonzom, Armant, O., Car, C., [...], Gardette, V., [...], Simon L., [...], Mondy, N. Environmental radioactivity impacts bioenergetic in tree frog of Fukushima. Environmental Pollution.. ⟨10.1016/j.envpol.2025.127147⟩2025 Secondi, J., Périsse, L., Lengagne, T., Mondy, N., 2025 - Differential responses of rural and urban populations to artificial light at night in the Spiny toad. Behavioral Ecology, 36 (4):1-11. ⟨10.1093/beheco/araf051⟩2023 Secondi, J., Scriba, M.F., Mondy, N., Lengagne, T. Artificial light at night decreases the pupillary light response of dark-adapted toads to bright light. Integrative Zoology, 18:867-875. (10.1111/1749-4877.12693)2023 Touzot, M., Dumet A., Secondi J., Lengagne T., Henri H., Desouhant E., Duchamp C., Mondy N., 2023 - Artifical light at night triggers slight transcriptomic effects on melatonin signaling but not synthesis in tadpoles of two anuran species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol, Part A, 280, 111386. (10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.111386)
2022 Cordonnier, M., Kaufmann, B., Simon, L., Escarguel, G., Mondy, N., 2022 - Discrimination of conspecifics from heterospecifics in a hybrid zone: Behavioral and chemical cues in ants. Insect Science, 29 (1), pp.276-288. ⟨10.1111/1744-7917.12915⟩2022 Gippet, JMW, Rocabert, C., Colin, T., Grangier, J., Tauru, H., Dumet, A., Mondy, N., Kaufmann, B., 2022 - The observed link between urbanization and invasion can depend on how invasion is measured –Diversity and Distributions, 28 : 1171-1179. (DOI: 10.1111/ddi.13509)2022 Touzot, M., Lefebure, T., Lengagne, T., Secondi, J., Dumet, A., Konecny-Dupré, L., Veber, P., Navratil, V., Duchamp, C., Mondy N., 2022 - Transcriptome-wide deregulation of gene expression by artificial light at night in tadpoles of common toads. Science of the Total Environment, 818, pp.151734. ⟨10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151734⟩2021 Gippet, J.M.W., Colin, T., Grangier, J., Winkler, F., Haond, M., Dumet, A., Tragust, S., Mondy, N., Kaufmann, B., 2021 - Land-cover and climate factors contribute to the prevalence of the ectoparasitic fungus Laboulbenia formicarum in its invasive ant host Lasius neglectus. Fungal Ecology 51, 101045. ⟨10.1016/j.funeco.2021.101045⟩
2021 Mondy, N., Boisselet, C., Poussineau, S., Vallier, F., Lengagne, T., Secondi, J., Romestaing, C., Geay, M., Puijalon, S., 2021 - Herbivory increases on freshwater plants exposed to artificial light at night. Aquatic Botany, 175, pp.103447. ⟨10.1016/j.aquabot.2021.103447⟩2021 Secondi, J., Mondy, N., Gippet, J.M.W., Touzot, M., Gardette, V., Guillard, L., Lengagne, T., 2021 - Artificial light at night alters activity, body mass, and corticosterone level in a tropical anuran. Behavioral Ecology, 32(5) : 932-940. ⟨10.1093/beheco/arab044⟩2021 Segrestin, J., Mondy, N., Boisselet, C., Guigard, L., Lengagne, T., Poussineau, S., Secondi, J., Puijalon, S., 2021 - Effects of artificial light at night on the leaf functional traits of freshwater plants. Freshwater Biology, 66, 2264-2271. ⟨10.1111/fwb.13830⟩2020 Mathiron, A.G.E., Dixneuf, C., Mondy, N., Lécureuil, C., Earley, R.L., Goubault, M., 2020 - Ecdysteroids affect female reproductive status and outcome of contest over hosts in the parasitoid wasp Eupelmus vuilleti. Hormones and Behavior, 125, 104819.2020 Secondi, J, Davranche, A, Théry, M, Mondy, N, Lengagne, T., 2020 - Assessing the effects of artificial light at night on biodiversity across the latitudinal gradient – current knowledge gaps. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29 : 404-419.2020 Touzot, M., Lengagne, T., Secondi, J., Desouhant, E., Théry, M., Dumet, A., Duchamp, C., Mondy, N., 2020 - Artificial light at night alters the sexual behaviour and fertilisation success of the common toad. Environmental Pollution, 259, 113883.
2019 Desouhant, E., Gomes, E., Mondy, N., Amat, I., 2019 - Mechanistic, ecological, and evolutionary consequences of artificial light at night for insects: review and prospective. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 167(1) : 1–22.2019 Dutour, M., Léna, J.P., Dumet, A., Gardette, V., Mondy, N., Lengagne, T., 2019 - The role of associative learning process on the response of fledgling great tits (Parus major) to mobbing calls. Animal Cognition, 22(6):1095–1103.2019 Touzot, M., Teulier, L., Lengagne, T., Secondi, J., Théry, M., Libourel, P.A., Guillard, L., Mondy, N., 2019 - Artificial light at night disturbs the activity and energy allocation of the common toad during the breeding period. Conservation Physiology, 7 : 1-9.2017 Cayuela, H., Léna, J.P., Lengagne, T., Kaufmann, B., Mondy, N., Konecny, L., Dumet, A., Vienney, A., Joly, P., 2017 - Relatedness predicts male mating success in a pond-breeding amphibian. Animal Behaviour, 130 : 251-261.2017 Desprat, J.L., Lengagne, T., Mondy, N., 2017 - Immune challenges and visual signalling in tree frogs. The Science of Nature, 104(21) : 1-9.2017 Desprat, J.L., Mondy, N., Lengagne, T., 2017 - Does testosterone affect foraging behavior in male frogs ? Hormones and Behavior, Hormones and Behavior, 90 : 25–30.2017 Desprat, J.L., Teulier, L., Puijalon, S., Dumet, A., Romestaing, C., Tattersall, G.J., Lengagne, T., Mondy, N., 2017 - Doping for sex: bad for mitochondrial performances ? Case of testosterone supplemented Hyla arborea during the courtship period. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, 209 : 74-83.2017 Gippet, Jérôme M.W., Mondy, Nathalie, Diallo-Dudek, Julita, Bellec, Arnaud, Dumet, Adeline, Mistler, Lubiana, Kaufmann, Bernard, 2017 - I’m not like everybody else: urbanization factors shaping spatial distribution of native and invasive ants are species-specific. Urban Ecosystems, 20 : 157–169.2017 Secondi, J., Dupont, V., Davranche, A., Mondy, N., Lengagne, T., Théry, M., 2017 - Variability of wetland surface and underwater nocturnal spectral irradiance with the presence of clouds in urban and peri-urban wetlands. PLoS ONE 12(11), e0186808 : 1-13.2017 Troïanowski, M., Mondy, N., Dumet, A., Arcanjo, C., Lengagne, T., 2017 - Effects of traffic noise on tree frog stress levels, immunity, and color signaling. Conservation Biology, 31(5) : 1132-1140.2016 Abidi, S., Abbaci, K., Geffard, O., Boumaiza, M., Dumet, A., Garric, J., Mondy, N., 2016 - Impact of cadmium on the ecdysteroids production in Gammarus fossarum. Ecotoxycology, 25 : 880-887.2016 Plantamp, C., Salort, C., Gibert, P., Dumet, A., Mialdea, G., Mondy, N., Voituron, Y., 2016 - All or nothing: Survival, reproduction and oxidative balance in Spotted Wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii) in response to cold. Journal of Insect Physiology 89 : 28–36.2015 Desprat, J.L., Lengagne, T., Dumet, A., Desouhant, E., Mondy, N., 2015 - Immunocompetence handicap hypothesis in tree frog: trade-off between sexual signals and immunity ? Behavioral Ecology, 26(4) : 1138–1146.2015 Josserand, R., Troïanowski, M., Grolet, O., Desprat, J.L., Lengagne, T., Mondy, N., 2015 - A phytohaemagglutinin challenge test to assess immune responsiveness of European tree frog Hyla arborea. Amphibia-Reptilia 36 : 111-118.
2015 Troïanowski, M., Condette, C., Mondy, N., Dumet, A., Lengagne, T., 2015 - Traffic noise impact stress and coloration but not calls in the European treefrog (Hyla arborea). Behaviour, 152 : 821-836
2014 Mondy, N., Grossi, V., Cathalan, E., Delbecque, J.P., Mermillod-Blondin, F., Douady, C.J., 2014 - Sterols and steroids in a freshwater crustacean (Proasellus meridianus) : hormonal response to nutritional input. Invertebrate Biology, 133(1) : 99-107.
2012 Mondy, N., Rey, B., Voituron, Y., 2012 - The proximal costs of case construction in caddisflies: antioxidant and life history responses. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 215 : 3453-3458.
- Autres productions 2013 - Corio-Costet M-F, Mondy N. Besoins nutritifs de l’insecte phytophage. Dans Sauvion N., Calatayud P., Thiéry D. & Marion-Poll F., Interactions insectes-plantes, Quae & IRD Editions, p. 95-104.2011
Mondy N., Cathalan E., Hemmer C., Voituron Y. 2011. Energetic cost of case construction in a caddisfly, Limnephius rhombicus: direct impacts on larvae and delayed impacts on the adults. Journal of Insect Physiology, 57, 197-202.
2009
Bodin A., Jaloux B., Delbecque J.P., Monge J.P., Mondy N. 2009. Reproduction in an unpredictable environment: how a parasitoid wasp, Eupelmus vuilleti, adjust oogenesis. Journal of Insect Physiology, 55, 643-648.
Statzner B., Mondy N.. 2009. Variation of colour patterns in larval Hydropsyche (Trichoptera): Implications for species identifications and the phylogeny of the genus. Limnologica, 39, 177-183.
Bel-Venner M.C., Mondy N., Arthaud F., Marandet J., Giron D., Venner S., Menu F. 2009. Ecophysiological attributes of adult overwintering in insects: insights from a field study in the nut weevil Curculio nucum. Physiological Entomology, 34, 61-70.
2007
Bodin A., Jaloux B., Mandon N., Vannier F., Delbecque J.P., Monge J.P., Mondy N. 2007. Host-induced ecdysteroids in the stop-and-go oogenesis in a synovigenic parasitoid wasp. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 65, 103-111.
2006
Mondy N., Corio-Costet M.F., Bodin A., Mandon N., Vannier F., Monge J.P. 2006. Importance of sterols acquired through host feeding in synovigenic parasitoid oogenesis. Journal of Insect Physiology, 52, 897-904
2005
Thibout E., Pierre D., Mondy N., Lecomte C., Biémont J-C., Auger J. 2005. Host-finding by the Asparagus fly, Platyparea poeciloptera, a monophagous Tephritid. Bull. Entomological res., 95, 1-7
Jaloux B., Errard C., Mondy N., Vannier F., Monge JP. 2005. Sources of chemical signals which enhance multiparasitism preference by a cleptoparasitoid. J. Chemical Ecol., 31, 1325-1337
Dugravot S., Mondy N., Mandon N., Thibout E., 2005. Increase of sulfur allelochemicals production in the leek Allium porrum in response to specialist insect attacks. J. Chemical Ecol., 31, 1287-1302
2004
Mondy N., Corio-Costet M-F. 2004. Feeding insects with a phytopathogenic fungus influences their diapause and population dynamics. Ecological Entomol., 17, 6, 793-808
Arnault I., Mondy N., Diwo S., Auger.J. 2004. Soil behaviour of sulfur natural fumigants as methyl bromide substitutes, Int. J. Env. Analitical chem., 84, 1-3, 75-82
2002
D'ettore P., Mondy N., Lenoir A, Errard C. 2002. Blending in with the crowd: social parasites integrate into their host colonies using a flexible chemical signature. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, 269, 1911-1918
Mondy N., Duplat D., Christides JP, Arnault I., Auger J. 2002. Aroma analysis of fresh and preserved onions and leek by dual SPME-Liquid extraction/GC/MS. J. Chromatogr. A, 963, 89-93
2001
Teyssier C., Amiot M-J., Mondy N., Auger J., Kahane R., Siess M-H. 2001. Effect of onion consumption by rats on hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes. Food Chemical Toxicol., 39, 981-987
Mondy N., Naudin A., Christides J.P., Mandon N., Auger J. 2001. Comparison between GC-MS and HPLC in Allium volatiles analysis. Chromatographia, 53, 356-360
2000
Mondy N., Corio-Costet M-F. 2000. Response to dietary phytopathogenic fungus (Botrytis cinerea) in grape berry moth (Lobesia botrana): the significance of fungus sterols. J. Insect Physiol., 46, 1557-1564
Arnault I., Mondy N., Cadoux F., Auger J. 2000. Possible interest of various sample transfer techniques for fast GC-MS analysis of true onion volatiles. J. Chromatogr. A, 896, 177-124
1998
Mondy N., Charrier B., Fermaud M., Pracros P., Corio-Costet M-F., 1998. Mutualism between a phytopathogenic fungus (Botrytis cinerea) and a vineyard pest (Lobesia botrana) : Positive effects on insect development and oviposition behaviour. Compte Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences (série III), 321 : 665-671
Mondy N., Pracros P., Fermaud M., Corio-Costet M-F., 1998. Olfactory and gustatory behaviour of Lobesia botrana in response to Botrytis cinerea. Entomologia Exp. App., 88: 1-7
1997
Mondy N., Caïssa C., Pitozet N., Delbecque J-P., Corio-Costet M-F., 1997. Effects of the ingestion of Serratula tinctoria extracts, a plant containing phytoecdysteroids, on the development of the vineyard pest Lobesia botrana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol., 35: 227-235 - Desprat, J.L., 2016 - When Ecology and Behaviour meet: Introduction to the special section on the Ecology and Behaviour Meeting 2016. Animal Biology 66: 401–402.
Chapitre d'ouvrage
2013
Corio-Costet M-F, Mondy N., 2013 - Besoins nutritifs de l’insecte phytophage. Dans Sauvion N., Calatayud P., Thiéry D. & Marion-Poll F., Interactions insectes-plantes, Quae & IRD Editions, p. 95-104.